Available analyses
PMM: The metabolism-metabolome platform of IPS2
Themes of researchs:
The Platform is a support to the researches on the primary metabolism (carbon, nitrogenous and sulphurated metabolites) and secondary metabolism (specialized metabolites) of plants and their answers to environmental requirements. The role of the Platform consists of the establishment of metabolic profiles (GC-MS, LC-MS), the identification of unknown compounds or/and the quantification (RMN, LC), the possible determination of their isotopic composition (IRMS and GC-C-IRMS) and feeding follow-up (RMN).
GC-MS:
- Profiling of primary metabolites
The GC-MS analysis can allow the identification of a large number of metabolites (700 metabolites in the library) but before an extraction from a matrix is mandatory. The separation of the compound is done by gas-chromatography.
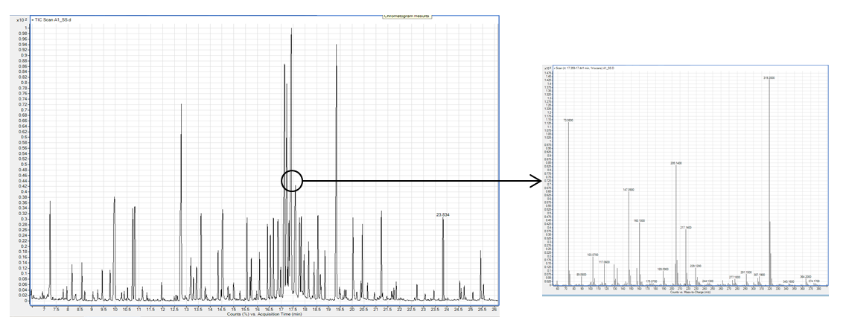
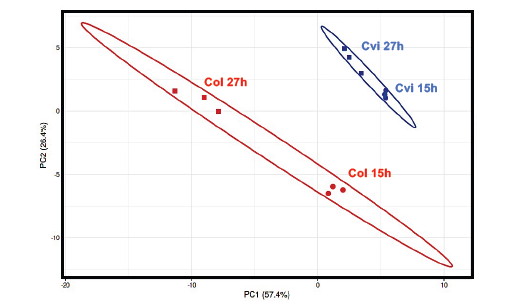
This technology allows to realize metabolomics profils of low molecular weight compounds like organic acids , amino acids, mono and disaccharides ...) and to have a relative quantification. All the data can be process with Mev software and we can apply a statistical treatment to see if they are possible correlations.
- Quantification of specific compound
The platform can develop analyses for a specific class of metabolites (terpenes, alcanes, fatty acids, aromas, volatils compounds…)
LC:
According to the application, LC analysis allows the absolute quantification of class of metabolite.
The applications are:
- Amino Acids (proline excepted)
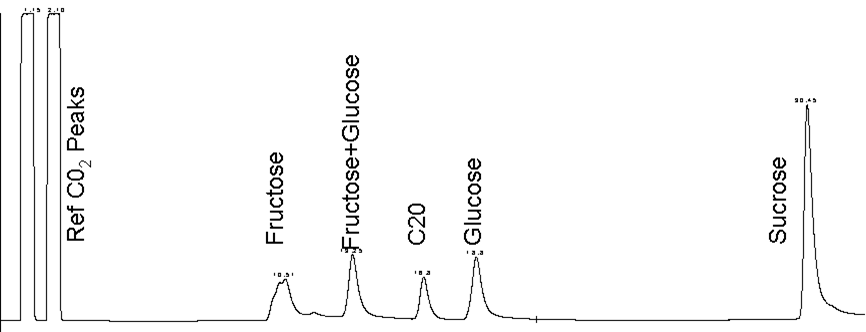
- Sugar (Sucrose, Glucose and Fructose)
- Cations (Li+,Na+,NH4+,K+,Mg+,Ca+)
- Anions (F-, Cl-,NO2-,Br-,NO3-,P-,SO3-)
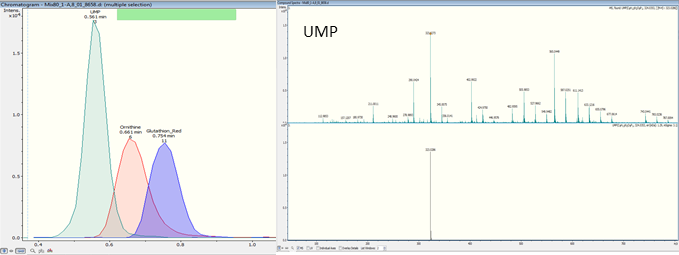
- LC-MS and LC-MS-MS:
LC-MS analysis allows the absolute quantification of 25 cofacteurs-nucleotides. Nevertheless they must be extracted from the matrix by SPE (solid phase extraction). Liquid chromatography separate the various métabolites presents in sample and the mass spectrometer (Q-TOF) identify and quantify them by an exact mass of specific fragmentation ion.
IRMS:
We have two isotopic mass spectrometers (IRMS) and several systems making it’s possible to obtain a pure gas from solid, liquid and gaseous samples. The isotopic mass spectrometers measure the isotopic report (13C/12C, 15N/14N, 18O/16O) of a pure gas (CO2, N2, O2) from solid, liquid or gaseous samples and compare it to gas reference (calibrate to the international standard).
- EA-IRMS:
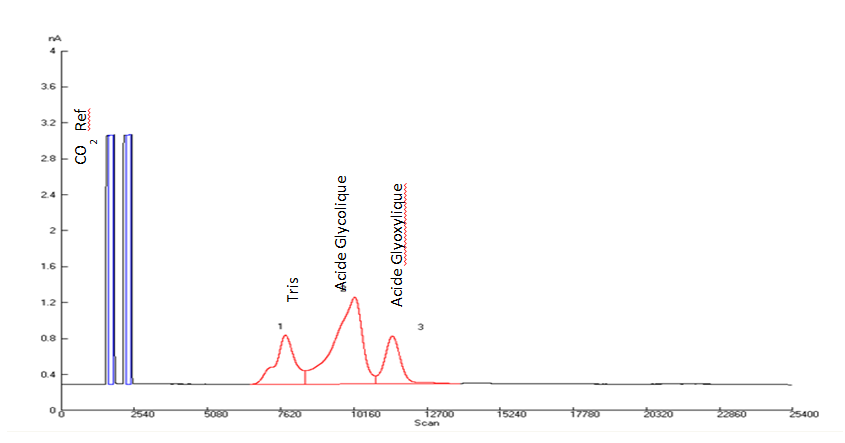
This is the technique for the isotopic analysis (13C/12C, 15N/14N) of some total organic matter (vegetable or animal dry powder) or metabolites cleansed by HPLC (eg amino acids, organic acids, soluble sugars).
- GC-C-IRMS or LC-co-IRMS:
These couplings allow the isotopic analysis of compound-specific, extracted from plant leaves for example, and separated by techniques of chromatographies (liquid or gaseous)
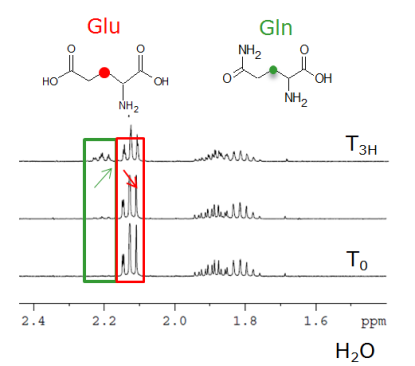
NMR:
NMR analysis allows the acquisition of experiences 1D H, 13C and 15N and\or 2D HSQC, COSY. These acquisitions can allow the absolute quantification in the matrix (enzymatic Activity), the structural identification or to follow an isotopic enrichment in the intramolecular positions