Single nuclei analysis of symbiotic nodulation
Cell-specific pathways recruited for symbiotic nodulation in the Medicago truncatula legume
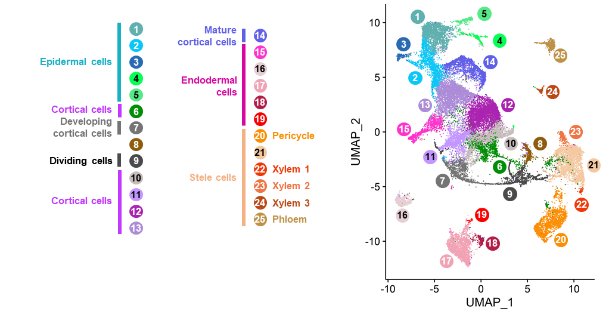
Medicago truncatula is a model legume species that has been studied for decades to understand the symbiotic relationship between legumes and soil bacteria collectively named rhizobia. This symbiosis called nodulation is initiated in roots with the infection of root hair cells by the bacteria as well as the initiation of nodule primordia from root cortical, endodermal, and pericycle cells, leading to the development of a new root organ, the nodule, where bacteria fix and assimilate the atmospheric dinitrogen for the benefit of the plant. In a collaborative study between the team SILEG at IPS2 and Marc Libault (University of Nebraska), published in Molecular Plant, we report the isolation and use of nuclei from mock and rhizobia-inoculated roots to conduct single nuclei RNA-seq (sNucRNA-seq) experiments. A gene expression map of the Medicago root was generated, comprising 25 clusters, which were annotated as specific cell types using 119 Medicago marker genes and orthologs to Arabidopsis cell-type marker genes. A focus on root hair, cortex, endodermis, and pericycle cell types, showing the strongest differential regulations in response to a short-term (48 hours) rhizobium inoculation, revealed both known genes and functional pathways, validating the sNucRNA-seq approach, but also numerous novel genes and pathways, allowing a comprehensive analysis of early root symbiotic responses at a cell-type-specific level.
15/11/2022
